Weak antibody response yet robust cellular immunity identified in children after SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection biorxivpreprint unibirmingham SARSCoV2 COVID19 AntibodyResponse CellularImmunity Omicron Variant Children
By Bhavana KunkalikarJul 28 2022Reviewed by Aimee Molineux In a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* preprint server, researchers assessed the antibody response and cellular immunity induced by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron infection in children.
The team assessed the neutralizing ability of sera obtained from individuals who reported a natural infection with SARS-CoV-2 variants, which were predominant before Omicron. Antibody binding ability to the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type and Omicron spike and receptor-binding domain regions was estimated in serological samples collected from 54 children aged between five and 15, infected with a pre-Omicron variant.
Results The study results showed that the relative antibody binding activity to the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron S and RBD declined remarkably in children as well as adults in comparison to that of the wild-type strain. The relative binding decreased by 85% in children and 88% in adults, while only 41% exhibited a positive RBD response. This indicated that recognition of Omicron by the antibodies in sera after a pre-Omicron infection was noticeably lowered in children and adults.
Furthermore, weak neutralization activity was elicited by primary Omicron infection while only 53% of the infected children displayed detectable neutralization titers despite a previous infection. On the other hand, robust neutralization was noted after secondary infection with measurable neutralization titers.
Canada Latest News, Canada Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Comparing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 and BA.5 vaccine breakthrough infectionsComparing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 and BA.5 vaccine breakthrough infections medrxivpreprint irj_pt SARSCoV2 COVID19 Omicron Vaccine BreakthroughInfection
Comparing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 and BA.5 vaccine breakthrough infectionsComparing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 and BA.5 vaccine breakthrough infections medrxivpreprint irj_pt SARSCoV2 COVID19 Omicron Vaccine BreakthroughInfection
Read more »
 Nasal spray highly effective against HIV and SARS-CoV-2 in animal modelsNasal spray highly effective against HIV and SARS-CoV-2 in animal models HIV NasalSpray SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID ScienceTM kochinstitute MIT harvardmed
Nasal spray highly effective against HIV and SARS-CoV-2 in animal modelsNasal spray highly effective against HIV and SARS-CoV-2 in animal models HIV NasalSpray SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID ScienceTM kochinstitute MIT harvardmed
Read more »
 The kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibodies up to 21 months after infectionThe kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibodies up to 21 months after infection EIDjournal CDCgov MassGeneralNews harvardmed HHI SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid infection antibodies
The kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibodies up to 21 months after infectionThe kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibodies up to 21 months after infection EIDjournal CDCgov MassGeneralNews harvardmed HHI SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid infection antibodies
Read more »
 Does vaccine- or infection-induced immunity protect less well against infection by specific SARS-CoV-2 variants?Does vaccine- or infection-induced immunity protect less well against infection by specific SARS-CoV-2 variants? ScienceMagazine rivm COVID19 coronavirus covid SARSCoV2 infection vaccine vaccination
Does vaccine- or infection-induced immunity protect less well against infection by specific SARS-CoV-2 variants?Does vaccine- or infection-induced immunity protect less well against infection by specific SARS-CoV-2 variants? ScienceMagazine rivm COVID19 coronavirus covid SARSCoV2 infection vaccine vaccination
Read more »
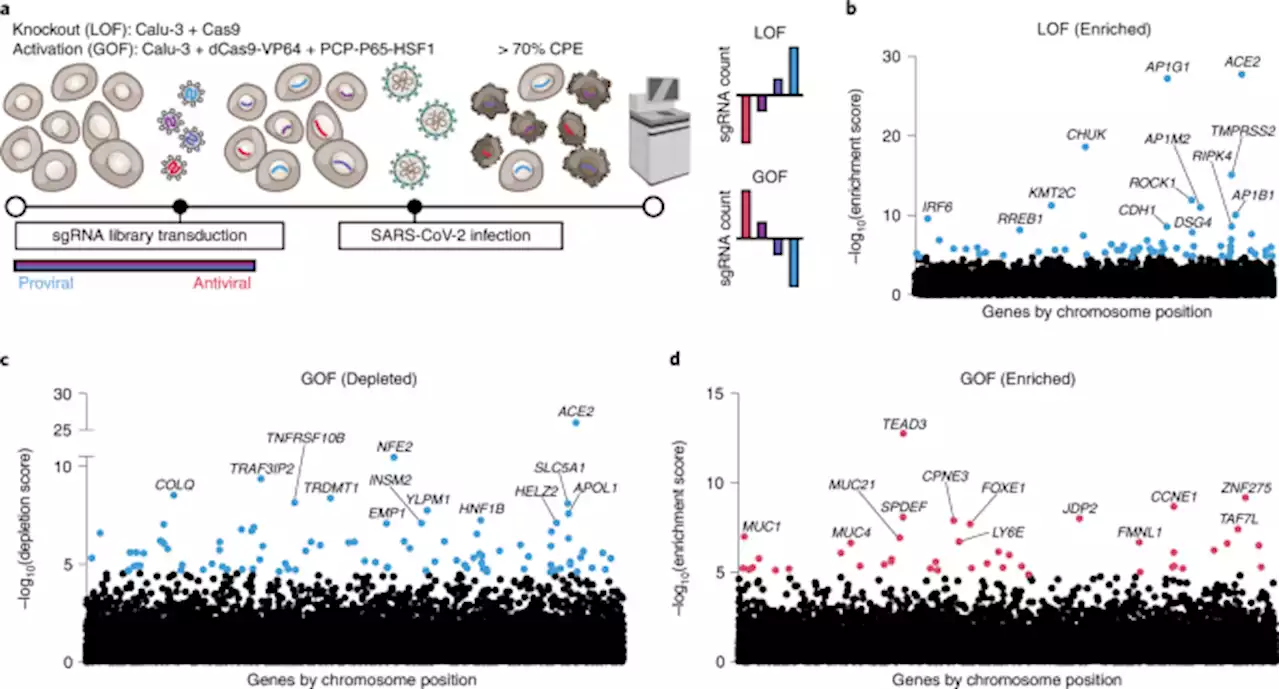 Genome-wide bidirectional CRISPR screens identify mucins as host factors modulating SARS-CoV-2 infection - Nature GeneticsGenome-wide CRISPR knockout and activation screens in human lung epithelial cells with endogenous expression of the SARS-CoV-2 entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 identify mucins as key host factors restricting viral infection.
Genome-wide bidirectional CRISPR screens identify mucins as host factors modulating SARS-CoV-2 infection - Nature GeneticsGenome-wide CRISPR knockout and activation screens in human lung epithelial cells with endogenous expression of the SARS-CoV-2 entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 identify mucins as key host factors restricting viral infection.
Read more »
 Study shows the emerging Omicron sublineage BA.2.75 does not show greater immune evasion than BA.5Study shows the emerging Omicron sublineage BA.2.75 does not show greater immune evasion than BA.5 biorxivpreprint karolinskainst UCT_news ETH Omicron SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid
Study shows the emerging Omicron sublineage BA.2.75 does not show greater immune evasion than BA.5Study shows the emerging Omicron sublineage BA.2.75 does not show greater immune evasion than BA.5 biorxivpreprint karolinskainst UCT_news ETH Omicron SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid
Read more »
