Could a common diabetes drug ease bipolardisorder?
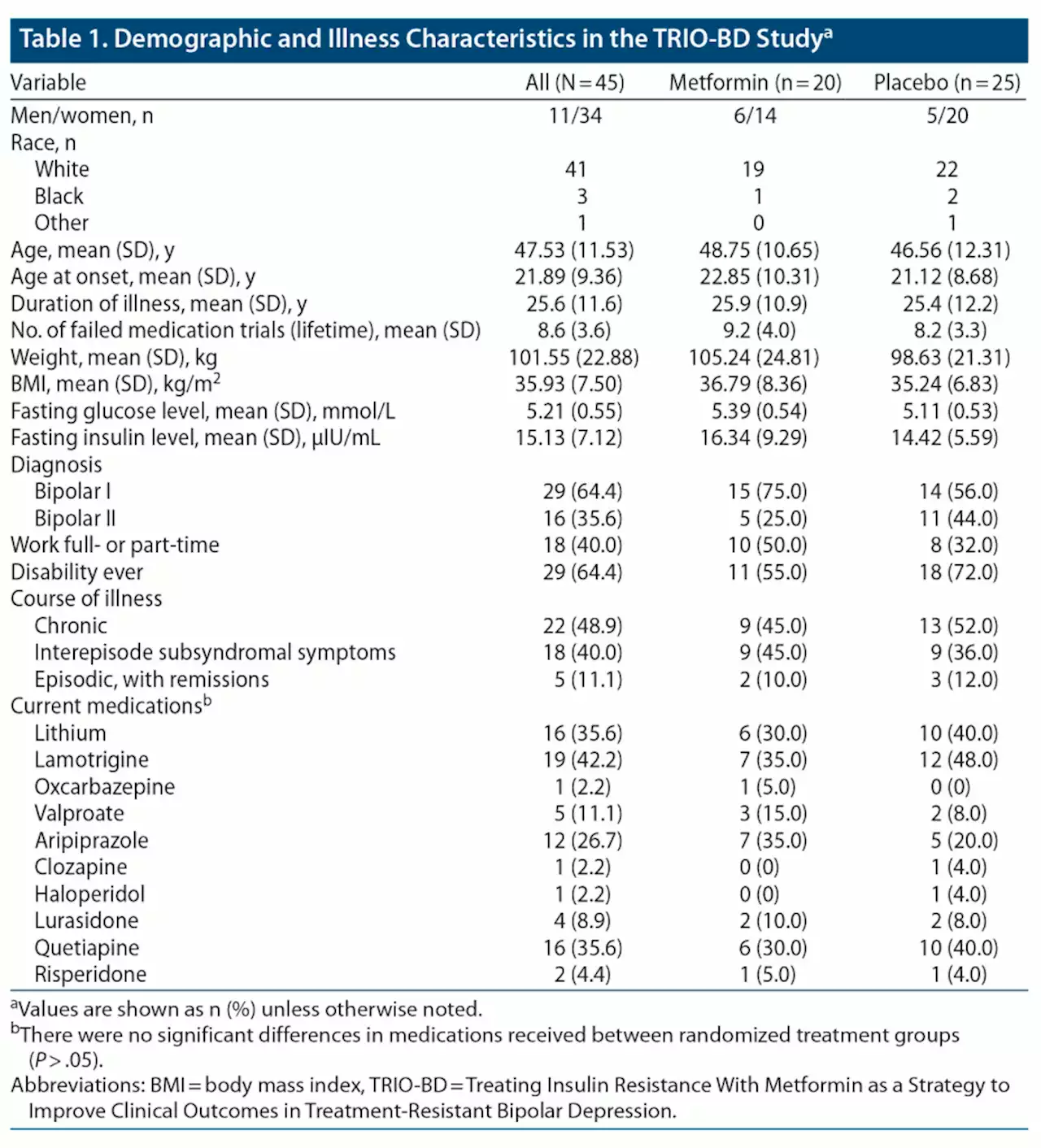
As hypothesized, successful reversal of IR by metformin resulted in a statistically significant and clinically meaningful reduction in depression rating scale scores in patients suffering from TRBD. Fifty percent of insulin-resistant TRBD patients treated with metformin converted to insulin-sensitive , and improvements in depression ratings that were first noted at 6 weeks were sustained up to 26 weeks.
No serious adverse events occurred over the course of this trial. Adverse events that did occur were primarily gastrointestinal symptoms commonly associated with metformin and were equally prevalent in the placebo group.found that BD patients with IR have equally poor outcomes as those with more advanced metabolic dysregulation .
Canada Latest News, Canada Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 SARS-CoV-2 oral vaccine candidate found to induce neutralizing mucosal IgASARS-CoV-2 oral vaccine candidate found to induce neutralizing mucosal IgA medrxivpreprint vaxart COVID19 Vaccine OralVaccine Trial SARSCoV2
SARS-CoV-2 oral vaccine candidate found to induce neutralizing mucosal IgASARS-CoV-2 oral vaccine candidate found to induce neutralizing mucosal IgA medrxivpreprint vaxart COVID19 Vaccine OralVaccine Trial SARSCoV2
Read more »
 What is the role of psychedelic drugs in the treatment of psychiatric disorders?A new study aimed to determine the clinical applications of psychedelic drugs along with psychedelic-assisted therapy for different psychiatric disorders.
What is the role of psychedelic drugs in the treatment of psychiatric disorders?A new study aimed to determine the clinical applications of psychedelic drugs along with psychedelic-assisted therapy for different psychiatric disorders.
Read more »
 Outdoor swimming to treat depression to be trialled as alternative to drugs
Outdoor swimming to treat depression to be trialled as alternative to drugs
Read more »
 The genetic heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms of relapsed refractory multiple myeloma - Nature CommunicationsThe genetic factors involved in disease progression and drug resistance in multiple myeloma (MM) are varied and complex. Here, genomic and transcriptomic profiling of 511 relapsed and refractory MM patients reveals genetic alterations in several oncogenic pathways contributing to progression and resistance to MM therapies.
The genetic heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms of relapsed refractory multiple myeloma - Nature CommunicationsThe genetic factors involved in disease progression and drug resistance in multiple myeloma (MM) are varied and complex. Here, genomic and transcriptomic profiling of 511 relapsed and refractory MM patients reveals genetic alterations in several oncogenic pathways contributing to progression and resistance to MM therapies.
Read more »
Rethinking the immunotherapy numbers gameImmunotherapies are a major breakthrough in oncology, yielding unprecedented response rates for some cancers. Especially in combination with conventional treatments or targeted agents, immunotherapeutics offer invaluable tools to improve outcomes for many patients. However, why not all patients have a favorable response remains unclear. There is an increasing appreciation of the contributions of the complex tumor microenvironment, and the tumor-immune ecosystem in particular, to treatment outcome. To date, however, there exists no immune biomarker to explain why two patients with similar clinical stage and molecular profile would have different treatment outcomes. We hypothesize that it is critical to understand both the immune and tumor states to understand how the complex system will respond to treatment. Here, we present how integrated mathematical oncology approaches can help conceptualize the effect of various immunotherapies on a patient’s tumor and local immune environment, and how combinations of immunotherapy and cytotoxic therapy may be used to improve tumor response and control and limit toxicity on a per patient basis.
Read more »