“This is important because there are very few risk indicators for dementia that can be identified as early as middle age,' researchers said.
Most adults need 7 or more hours of quality sleep each night, according to the National Institutes of Health. Kids and teens need even more.— even when they’re occurring decades before the disease sets in.by researchers at the University of Birmingham in the United Kingdom, looked at data from more than 600 adults in thebetween 35 and 64 years old and 2,600 adults aged 79 and older. The study collected data between 2002 and 2012.
"Interestingly, the study found that the associations were much stronger for men than for women," researchers said.
Canada Latest News, Canada Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Nightmares in Middle Age Linked to Increased Dementia RiskMost of us consider nightmares pretty harmless, but apparently, they can be a bad sign. According to research at the University of Birmingham, people who experience frequent bad dreams in middle age are more likely to be diagnosed with dementia later in life. New research suggests nightmares may
Nightmares in Middle Age Linked to Increased Dementia RiskMost of us consider nightmares pretty harmless, but apparently, they can be a bad sign. According to research at the University of Birmingham, people who experience frequent bad dreams in middle age are more likely to be diagnosed with dementia later in life. New research suggests nightmares may
Read more »
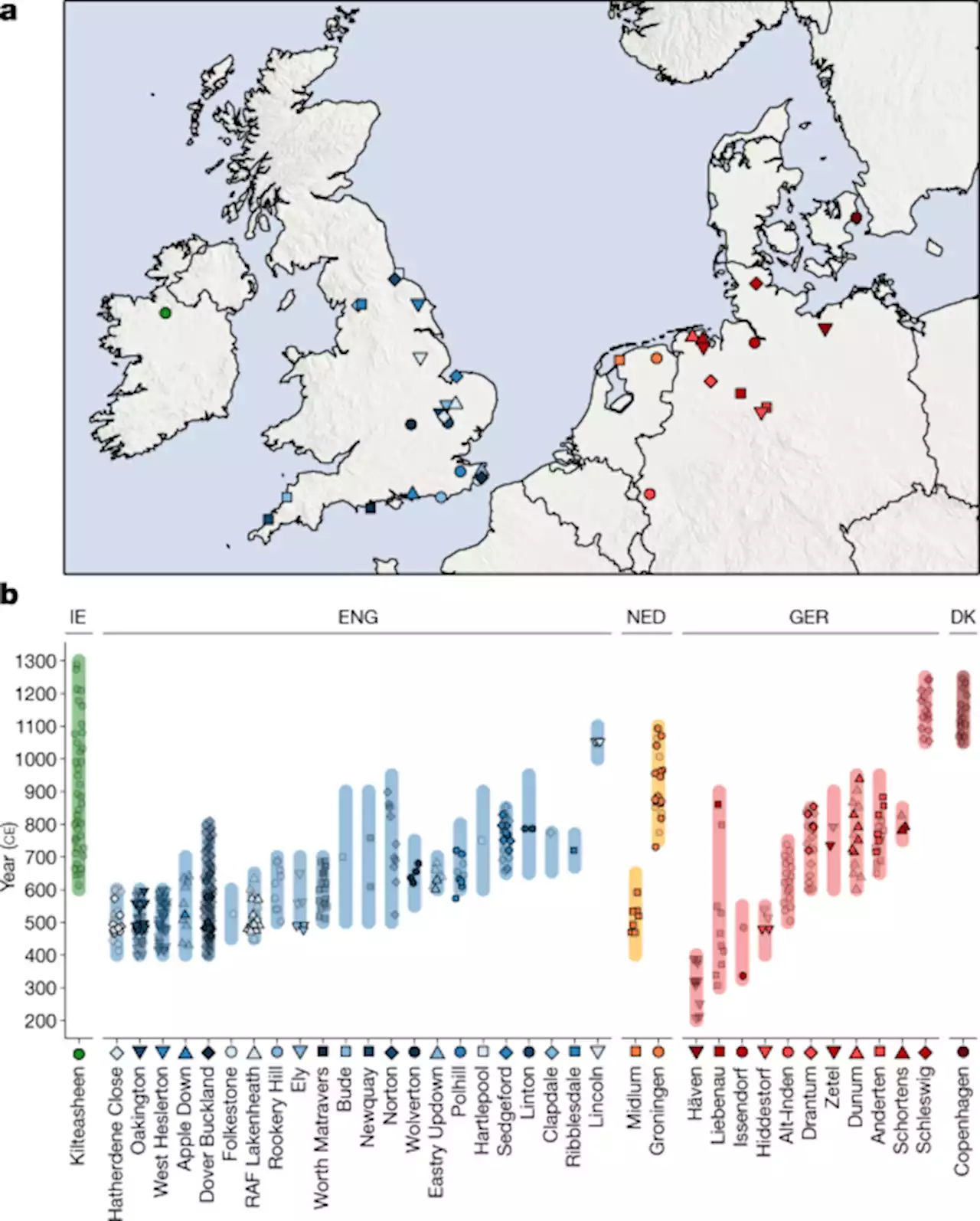 The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool - NatureArchaeogenetic study of ancient DNA from medieval northwestern Europeans reveals substantial increase of continental northern European ancestry in Britain, suggesting mass migration across the North Sea during the Early Middle Ages.
The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool - NatureArchaeogenetic study of ancient DNA from medieval northwestern Europeans reveals substantial increase of continental northern European ancestry in Britain, suggesting mass migration across the North Sea during the Early Middle Ages.
Read more »
 New Study to Investigate Overweight Fathers and Children's Dementia RiskProject will look at differences in brain structure, memory, and cognition in young people with overweight vs healthy weight fathers.
New Study to Investigate Overweight Fathers and Children's Dementia RiskProject will look at differences in brain structure, memory, and cognition in young people with overweight vs healthy weight fathers.
Read more »
 Herbert Protocol: Missing person scheme aims to save livesThe Herbert Protocol helps to trace people with dementia if they go missing.
Herbert Protocol: Missing person scheme aims to save livesThe Herbert Protocol helps to trace people with dementia if they go missing.
Read more »
 New microprotein linked to Alzheimer's risk discovered during USC studyThe protein, called SHMOOSE, is a 'microprotein' encoded by a newly discovered gene within the cell's energy-producing mitochondria, researchers said. A mutation within the gene partially inactivates the SHMOOSE microprotein and is associated with a 30% higher risk for Alzheimer's disease across four different cohorts.
New microprotein linked to Alzheimer's risk discovered during USC studyThe protein, called SHMOOSE, is a 'microprotein' encoded by a newly discovered gene within the cell's energy-producing mitochondria, researchers said. A mutation within the gene partially inactivates the SHMOOSE microprotein and is associated with a 30% higher risk for Alzheimer's disease across four different cohorts.
Read more »
