Detection of SARS-CoV-2 variants in aircraft wastewater Coronavirus Disease COVID SARSCoV2 wastewatermonitoring variantspread aircraft travel aviation surveillance VirusesMDPI univamu IHU_Marseille
By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.Jul 12 2022Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Scientists have worked relentlessly to contain the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 . To this end, several pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical strategies have been developed to prevent further transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and protect individuals from severe infection.
To date, most available studies have focused on the impact of travel restrictions on the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although some studies have shown that these restrictions significantly delayed viral transmission, others have contradicted these observations and instead reported that travel restrictions were inadequate to preventing global transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
In fact, several studies have successfully isolated viral genotypes circulating within a community by sequencing the SARS-CoV-2 genome from sewage samples. About the study A new Viruses study successfully detected SARS-CoV-2 variants in the wastewater of aircrafts. Herein, researchers obtained wastewater samples from two flights traveling from Addis Ababa, Ethiopia to Marseille, France.
Taken together, 12 passengers of the December 24, 2021 flight tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by a lateral flow test. Genomic sequencing of 11 of these samples confirmed the presence of the Omicron variant. Although the wastewater tanks were thoroughly cleaned between flights, the possibility of contamination by traces of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the blackwater tanks from previous flights cannot be entirely omitted. However, in this case, the high viral load cannot be the result of contamination and is strongly linked to viral excretion by onboard passengers or aircraft crew.
Canada Latest News, Canada Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 SARS-CoV-2 spike protein downregulates ACE2 expressionSARS-CoV-2 spike protein downregulates ACE2 expression SARSCoV2 COVID19 ACE2 SpikeProtein
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein downregulates ACE2 expressionSARS-CoV-2 spike protein downregulates ACE2 expression SARSCoV2 COVID19 ACE2 SpikeProtein
Read more »
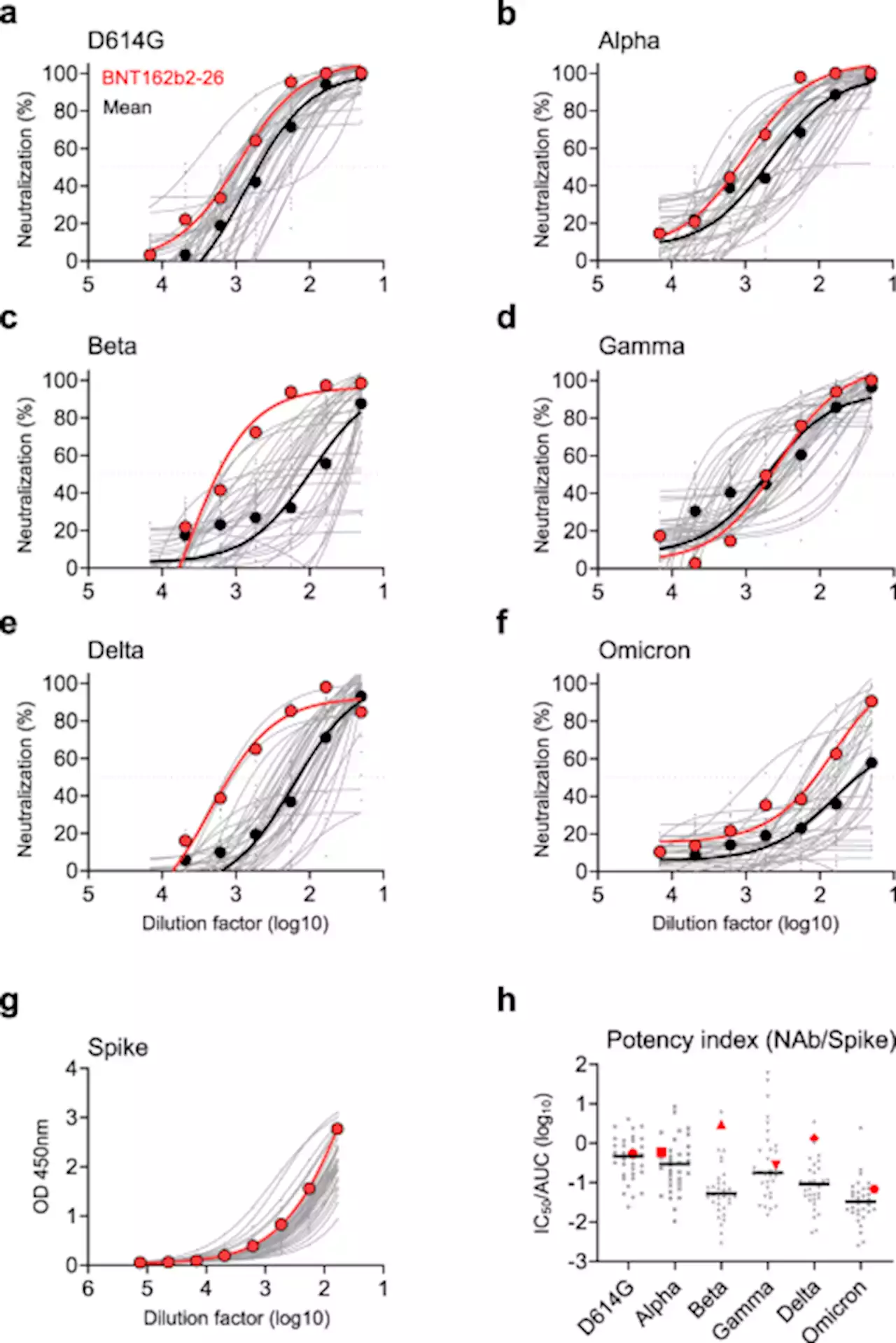 A broadly neutralizing antibody protects Syrian hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron challenge - Nature CommunicationsSARS-CoV-2 variants of concern such as the Omicron variant pose a challenge for vaccination and antibody immunotherapy. Here, Zhou et al. isolate a broadly neutralizing antibody (bNAb), named ZCB11, that protects Golden Syrian hamsters against Omicron. Applying CryoEM the authors show that ZCB11 heavy chain predominantly interacts with RBD in up confirmation, which interferes with ACE2 receptor binding.
A broadly neutralizing antibody protects Syrian hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron challenge - Nature CommunicationsSARS-CoV-2 variants of concern such as the Omicron variant pose a challenge for vaccination and antibody immunotherapy. Here, Zhou et al. isolate a broadly neutralizing antibody (bNAb), named ZCB11, that protects Golden Syrian hamsters against Omicron. Applying CryoEM the authors show that ZCB11 heavy chain predominantly interacts with RBD in up confirmation, which interferes with ACE2 receptor binding.
Read more »
 Stinging nettle extract inhibits SARS-CoV-2 cell fusionIn a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* preprint server, researchers at Ghent University and KU Leuven, Belgium, demonstrated that Urtica dioica agglutinin (UDA), a monomeric lectin extracted from stinging nettle rhizomes, inhibited severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VOCs) cell to cell fusion.
Stinging nettle extract inhibits SARS-CoV-2 cell fusionIn a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* preprint server, researchers at Ghent University and KU Leuven, Belgium, demonstrated that Urtica dioica agglutinin (UDA), a monomeric lectin extracted from stinging nettle rhizomes, inhibited severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VOCs) cell to cell fusion.
Read more »
 Scientists explore antigenic imprinting in SARS-CoV-2A recently published study compared monoclonal RBD antibody responses induced by SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant infections to antibodies induced by the ancestral virus in immunologically naive subjects.
Scientists explore antigenic imprinting in SARS-CoV-2A recently published study compared monoclonal RBD antibody responses induced by SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant infections to antibodies induced by the ancestral virus in immunologically naive subjects.
Read more »
 Production of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from hyperimmunized chickensProduction of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from hyperimmunized chickens Antibodies Coronavirus Disease COVID chickens neutralizing antibodies egg SARSCoV2 VirusesMDPI ucdavis UTSEngage GeorgeMasonU
Production of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from hyperimmunized chickensProduction of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from hyperimmunized chickens Antibodies Coronavirus Disease COVID chickens neutralizing antibodies egg SARSCoV2 VirusesMDPI ucdavis UTSEngage GeorgeMasonU
Read more »
 A broadly neutralizing antibody protects Syrian hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron challenge - Nature CommunicationsSARS-CoV-2 variants of concern such as the Omicron variant pose a challenge for vaccination and antibody immunotherapy. Here, Zhou et al. isolate a broadly neutralizing antibody (bNAb), named ZCB11, that protects Golden Syrian hamsters against Omicron. Applying CryoEM the authors show that ZCB11 heavy chain predominantly interacts with RBD in up confirmation, which interferes with ACE2 receptor binding.
A broadly neutralizing antibody protects Syrian hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron challenge - Nature CommunicationsSARS-CoV-2 variants of concern such as the Omicron variant pose a challenge for vaccination and antibody immunotherapy. Here, Zhou et al. isolate a broadly neutralizing antibody (bNAb), named ZCB11, that protects Golden Syrian hamsters against Omicron. Applying CryoEM the authors show that ZCB11 heavy chain predominantly interacts with RBD in up confirmation, which interferes with ACE2 receptor binding.
Read more »
